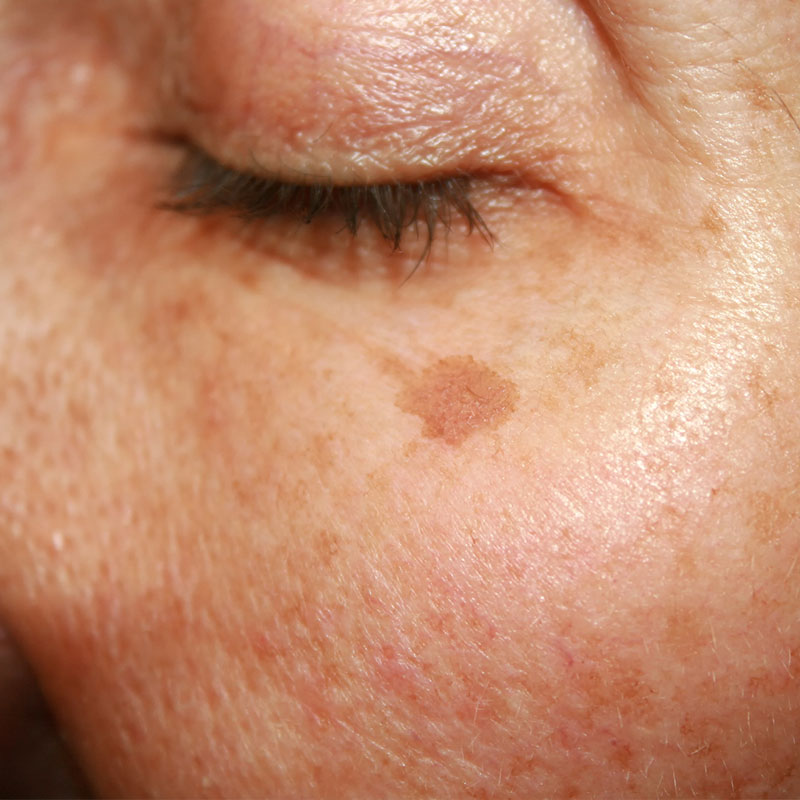
WHAT IS SKIN PIGMENTATION?
Skin Pigmentation Treatment – Skin pigmentation is when some areas of the skin appear darker than the rest. It occurs as small patches, that can sometimes cover large areas, all over the body. While Ski pigmentation isn’t necessarily a harmful condition of the skin, it could indicate the presence of other underlying health disorders.
Skin pigmentation occurs as a result of excessive melanin production in the skin. There are various factors that could lead to this overproduction:
- Medications of certain types have been found to cause extra production of melanin. Chemotherapy medication can also cause skin pigmentation.
- Pregnancy changes and/or hormonal changes have been observed to cause excess melanin production in women.
- Excessive exposure to the skin is another reason. The more your skin is exposed to the sun, the more tendency there is for the skin to produce extra melanin.
- A rare endocrine disorder, named Addison’s Disease, can cause skin pigmentation in regions that are most commonly exposed to the sun (face, neck, and hands), as well as exposed to friction (elbows and knees).
TYPES AND CAUSES OF SKIN PIGMENTATION
There are various types of skin pigmentation, the most common ones being the following:
- Melasma: This is usually caused by hormonal changes, and can be observed especially around the time of pregnancy. Those with Melasma can find areas of hyperpigmentation all over the body, but mainly in the stomach and face regions.
- Sunspots: This is a very common type of Skin pigmentation. Also known as Liver Spots or Solar Lentigines, this condition is caused by excessive sun exposure. Areas of pigmentation are those regions in the body where the skin is exposed to the sun, like the hands and face.
Post-inflammatory - Hyperpigmentation: This type of pigmentation appears as a side effect of an injury or inflammation on the skin. A well-known example of this is Acne.
SYMPTOMS OF SKIN PIGMENTATION
The main symptom of Skin pigmentation is the darkened patches of skin that can be observed on the body. These patches can be of any size, and can occur on any part of the body.
If you have pigmented skin, there are various things that could pose a potential risk to the pigmented areas, causing them to worsen. The biggest risks are sun excessive sun exposure and inflammation. These can cause extra melanin production in the skin, which is the main cause of Skin pigmentation.
Other risk factors depend upon the exact type of Skin pigmentation that you have. They could include:
- Pregnancy or the use of oral contraceptives
- Darker skin types, which are more prone to excessive melanin production
- Medication that may increase your skin’s light sensitivity
- Trauma to the skin, such as inflammation or other injuries
SKIN PIGMENTATION TREATMENT
For an accurate diagnosis, your medical history may be needed along with a physical exam. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be needed.
After this, you may be administered a topical medication that can treat most cases of Skin pigmentation. These medications will usually contain Hydroquinone, which helps lighten the skin. However, hydroquinone should only be used as per the prescribed frequency and dosage as excessive usage can lead to skin darkening instead. Other topical medication includes Retinoids, which can also help lighten dark spots. These medications can produce the wanted results but will only work over the span of a few months.
Home remedies can also be followed to help with hyperpigmentation. A major one is the daily use of sunscreens. The best kind of sunscreens is those that preferably contain zinc oxide as the main ingredient, has an SPF of 30 to 50, and has a broad-spectrum coverage. Recommended usage for sunscreens is a daily application, with a top-up every 2 hours if you are outdoors, or if you are sweating or swimming.
Home remedies can also be followed to help with hyperpigmentation. A major one is the daily use of sunscreens. The best kind of sunscreens is those that preferably contain zinc oxide as the main ingredient, has an SPF of 30 to 50, and has a broad-spectrum coverage. Recommended usage for sunscreens is a daily application, with a top-up every 2 hours if you are outdoors, or if you are sweating or swimming.
PREVENTING SKIN PIGMENTATION
Although not completely, the following preventive measures can protect your skin from adverse hyperpigmentation for the most part:
- Daily usage of sunscreen having an SPF of at least 30
- Wearing hats or other forms of clothing that can block sunlight
- Avoiding the sun during the day, when its rays are strongest
- Avoiding medications that may cause hyperpigmentation as a side effect
Skin pigmentation isn’t a harmful condition and could fade away on its own in most cases by following the right skincare habits. Sometimes, more aggressive treatment may be needed, but the skin pigmentation can be reversed exponentially.